SOM-DST

기존 모델의 문제점
Ontology-based DST
- 실제 시나리오에 잘 대응하지 못함
- unseen value를 처리할 수 없음
- ontology가 많으면 처리 시간이 오래 걸림
Open-vocab-based DST (TRADE)
- turn마다 slot의 모든 value를 생성해야해서 비효율적임
Definition
: turn
: slot
: corresponding slot value
: total number of such slots
: System response
: User utterance
State Operation Predictor (Encoder)
Encoder 모델로 pretrained BERT encoder 사용
Encoder Input을 만들기 위한 준비물
: dialogue utterances at turn t
;와 를 구분하기 위한 스페셜 토큰[SEP]dialogue turn이 끝났다는 것을 표시하기 위한 스페셜 토큰
: representation of the j-th slot-value pair
- j-th slot-value pair를 하나의 벡터로 aggregate
-
[SLOT] 이라는 스페셜 토큰을 사용
BERT의 [CLS] 토큰과 같은 역할
-
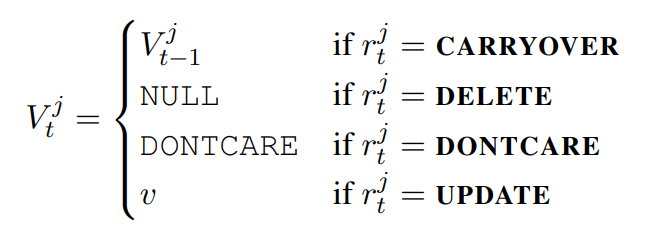
: representation of the dialogue state at turn t
Encoder Input
$$X_t = [CLS] ⊕ D_{t-1} ⊕D_t ⊕ B_{t-1}$$
segment id: 0 1 1⇒ Input : Sum( embedding, segment id embedding, positional embedding)
dialogue history로 이전 턴의 dialogue utterances 을 사용한다. dialogue history의 size: 1
모델이 입력으로 들어오는 dialogue 간의 Markov property를 가정
이전 turn dialogue state 은 전체 dialogue history를 압축적으로 표현하는 역할
Encoder Output
: 까지 집합
- 에 대응하는 output
- : 전체 input 를 sequence로 aggregate
- : feed-forward layer with a learnable parameter
State Operation Prediction
- : learnable parameter
- : j-th slot의 turn t에서의 연산에 대한 확률 분포
-
SOM-DST에서는 ,
→
→ slot의 Operation의 결과가 UPDATE 일 때 slot value를 generation
-
Encoder에서 나온 Operation의 결과가
Update인 경우를 집합으로 표현하면, and its size as
Recab for V
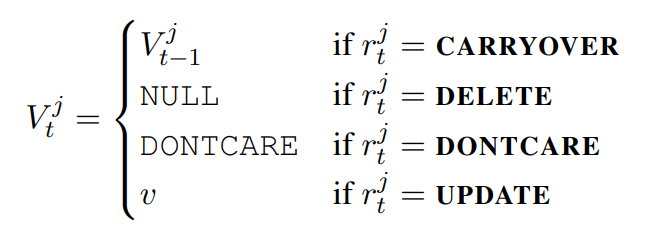
Slot Value Generator (Decoder)
- Encoder에서 나온 Operation의 결과가
Update인 경우 해당 slot의 value를 예측 -
SOM-DST의 generator는 value를 개가 아닌 개의 slot에 대해서만 만들어준다.
대부분의 경우에서 이기 때문에 더 효율적이라고 주장
-
Decoder 모델로 GRU 사용
- 입력으로 word embedding vector 를 받으면서 GRU의 hidden state vector 를 recurrent하게 업데이트
- , : GRU에 들어가는 초기값
- 가 [EOS] 토큰이 나올때까지 진행
-
hidden state 는 k-th decoding step을 거치면서 vocabulary 와 user utterance의 단어에 대한 확률 분포로 변함
-
: Encoder와 Decoder가 서로 공유하는 word embedding matrix
- : vocabulary size
- user utterance의 단어에 대한 확률 분포
: final output distribution
-
- : learnable parameter
- : context vector
-
Objective Function
State operation predictor
Main Task
state operation classification
Auxiliary Task
domain classification
state operation classification 외에도 domain classification을 보조 task로 사용하여 모델이 dialogue turn 간의 slot operation과 domain transition의 상관 관계를 학습하도록 함
- : learnable parameter
-
: turn t에서 domain에 대한 확률 분포
- : # of domains defined in the dataset
Average of the negative log-likelihood
- : one-hot vector for the ground truth domain
- : one-hot vector for the ground truth operation for the j-th slot
Slot value generator
Average of the negative log-likelihood
- : # of tokens of the ground truth value that needs to be generated for the j-th slot
- : one-hot vector for the ground truth token that needs to be generated for the j-th slot at the k-th decoding step
Final Loss
to minimized
Experimental Setup
Datasets
MultiWOZ 2.0 and MultiWOZ 2.1
Training
- Encoder : Bert-base-uncased
- Decoder : GRU
- Hidden size : 768
- Optimizer : BertAdam
- Encoder LR and warmup : 4e-5, 0.1
- Decoder LR and warmup : 1e-4, 0.1
- Batch size : 32
- Dropout : 0.1
- Word Dropout 적용, 0.1확률로 word 를 [UNK] 로 바꿈
- Input max length : 256
- Training Epoch : 30
결과
Joint Goal Accuracy
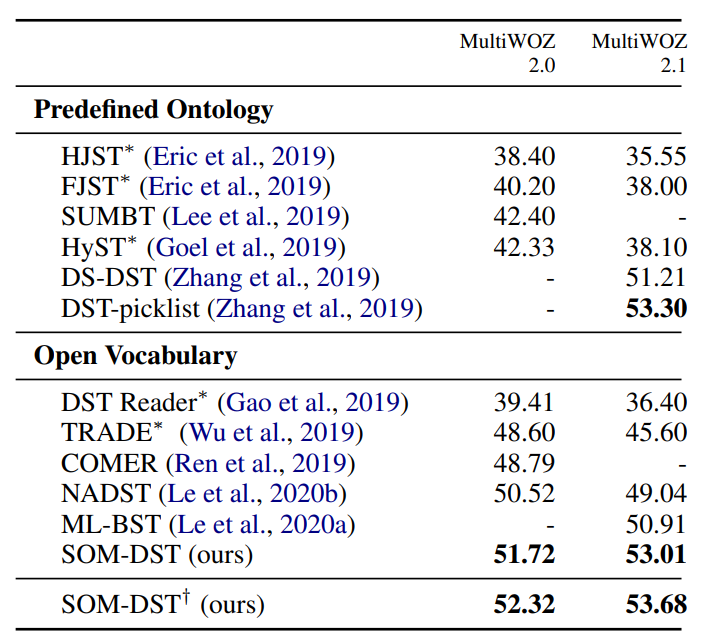
† indicates the case where BERT-large is used for our model
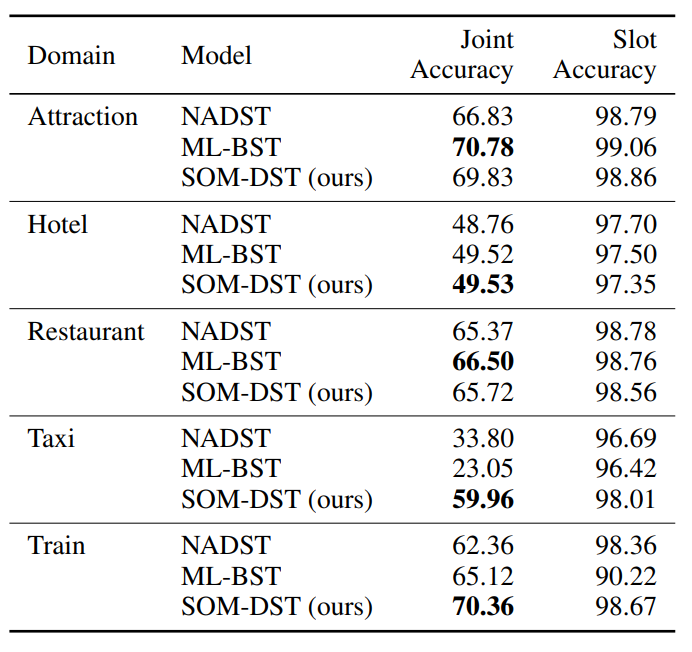
Domain-specific Accuracy
Latency
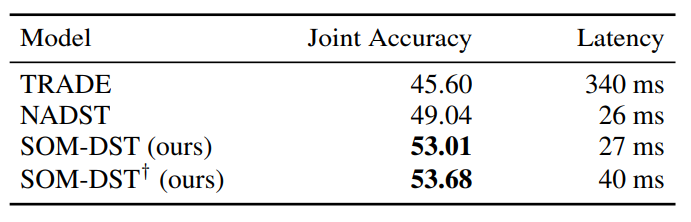
평가
- JGA, Domain-specific Accuracy 에서 SOTA 혹은 비슷한 수준의 성능을 보여줌
- inferecnce 타임이 매우 짧음에도 불구하고 좋은 성능을 보여줌